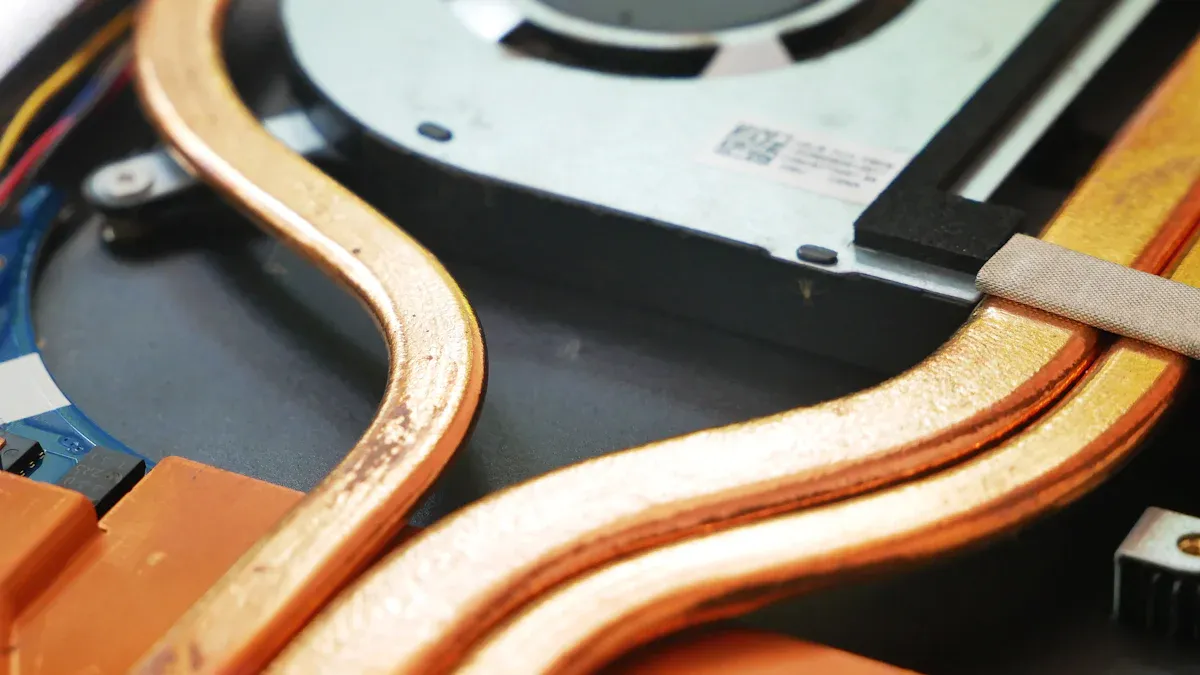

You might wonder if Heatpipe Cooling is right for you. This technology comes with some great perks, like small size and easy maintenance. You don’t need extra power, and you can count on it to work well. At the same time, you should know about the limits. Some users notice it only recovers sensible heat, and that can matter depending on your needs. Thinking about these ups and downs helps you choose what works best.
Heatpipe Cooling moves heat well without any moving parts. This makes it quiet and easy to take care of. It does not need much work to keep running.
This cooling method is small and light. It fits easily in tight places. You can use it in laptops and gaming consoles.
Heatpipe cooling costs more at first. But it can save you money later. It has low running costs and lasts a long time.
How you place your device matters. Heatpipe cooling works best when standing up. Think about how your device sits before you pick this system.
Heatpipe Cooling works well for devices that do not get very hot. It cools things without making noise like fans do.
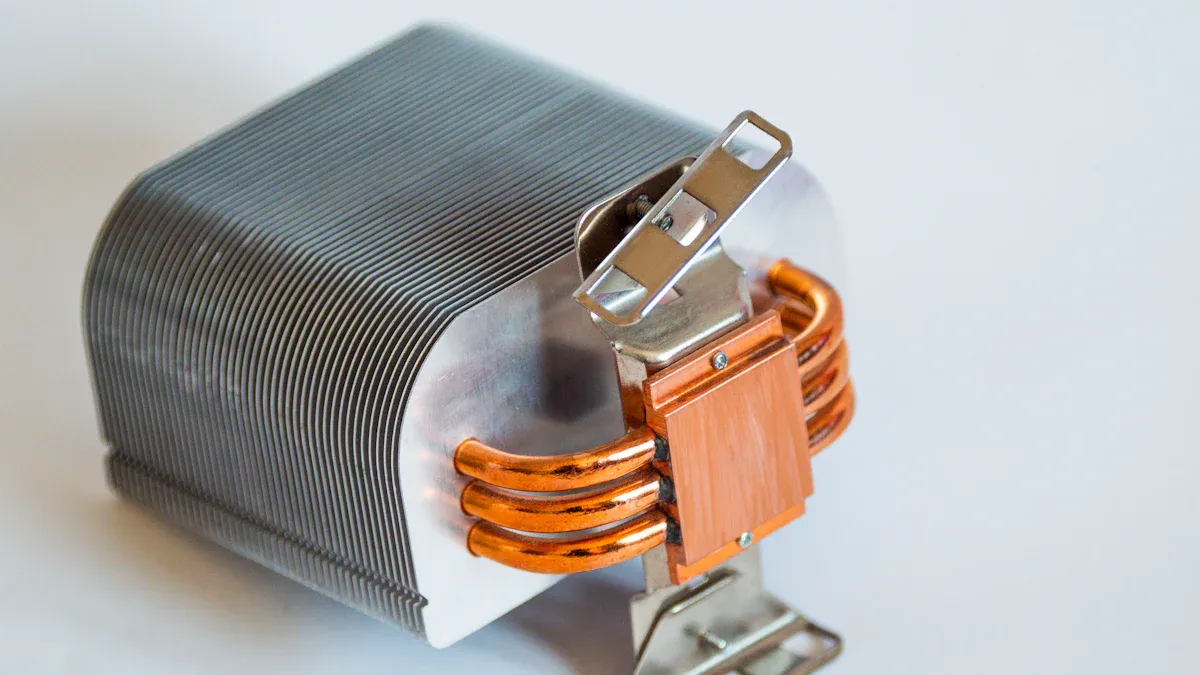
You might wonder how Heatpipe Cooling actually works. The secret lies in a simple but clever process. Inside each heat pipe, you find a small amount of liquid sealed in a closed tube. When one end of the pipe gets hot, the liquid turns into vapor. This vapor moves to the cooler end of the pipe, where it cools down and becomes liquid again. A special wick inside the tube helps pull the liquid back to the hot end, so the cycle keeps going. This process moves heat quickly from one place to another.
Here’s a quick look at the main parts:
|
Principle |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Working Fluid |
A small amount of liquid, often water, sealed inside a tube. |
|
Wick Structure |
A material that helps move the liquid back to the hot end. |
|
Heat Transfer |
Heat causes the liquid to turn into vapor and travel to the cool end. |
|
Cycle Continuation |
The liquid returns to the hot end, and the process repeats. |
Let’s break it down step by step:
The heat pipe contains a special fluid.
When the hot end heats up, the fluid turns into vapor.
The vapor travels to the cooler end of the pipe.
At the cool end, the vapor turns back into liquid and releases heat.
The wick pulls the liquid back to the hot end, starting the cycle again.
You don’t need to do anything to keep this process going. The heat pipe works on its own, moving heat without any moving parts or extra power.
You see Heatpipe Cooling in many places. It helps keep computers and laptops from overheating. You also find it in electronics like smartphones and gaming consoles. In factories, heat pipes help control the temperature of machines and equipment cabinets. Some common uses include:
Heat sinks that touch hot computer chips directly.
Tiny heat pipes built into devices to spread heat.
Large heat exchangers that cool down whole systems.
Tip: If you use a computer or game console, you probably already benefit from heat pipes without even knowing it!
You want your devices to stay cool. Heatpipe Cooling does this job well. It moves heat much faster than air cooling. Some heat pipes reach thermal conductivities of 860 W/(m·K). Air cooling systems are much lower. This means your computer can keep running smoothly. Even when things get hot, it works well.
Heat pipes use a process where liquid turns into vapor. Then it turns back into liquid. This helps them move heat quickly.
In one test, gravity-assisted heat pipes cooled 64.8% better than air-cooled heat sinks.
Here’s a table showing how temperature drops as heat load goes up:
|
Heat Load (W) |
Temperature Reduction (°C) |
|---|---|
|
80 |
3.8 |
|
90 |
5.7 |
|
100 |
6.5 |
|
120 |
7.7 |
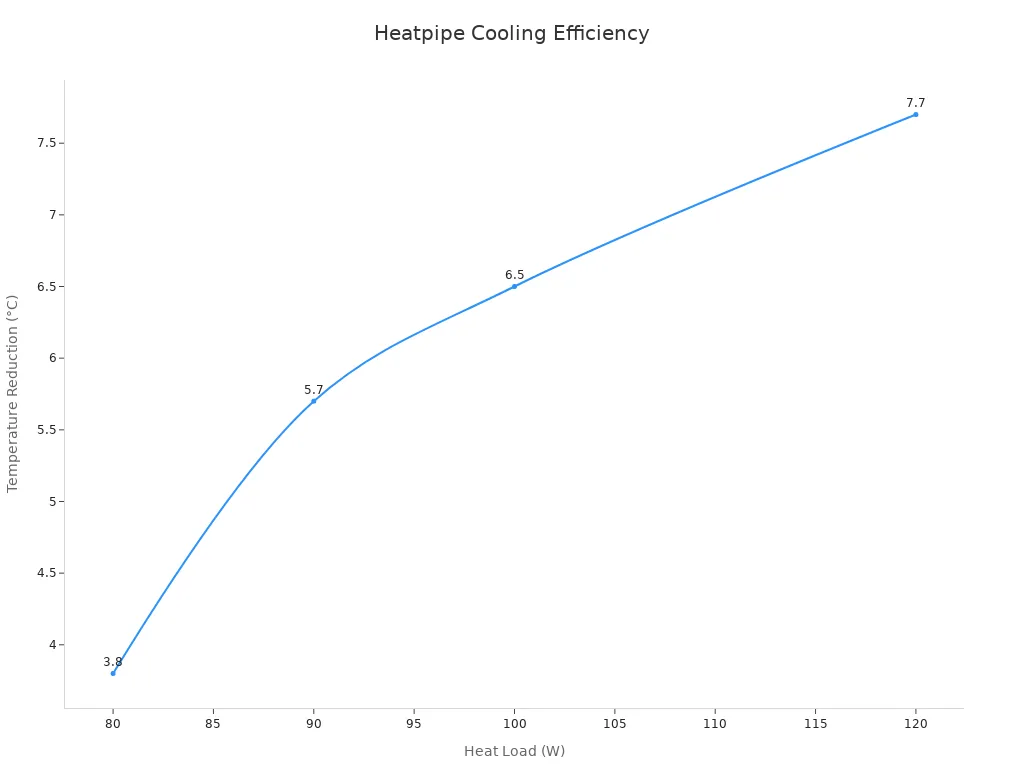
So, if you want a cooling system that keeps up, Heatpipe Cooling stands out.
Your device might have a strange shape or tight space. Heatpipe Cooling can fit almost anywhere. You can bend or flatten heat pipes to match your design. Some heat pipes can be flattened to 30%-60% of their size. You can also change the inside to make them work better for you.
|
Design Variation |
Impact on Performance |
|---|---|
|
Effective Thermal Conductivity |
Ranges from 10,000 to 100,000 W/m·K, much higher than solid metals. |
|
Internal Structure |
You can adjust the wick to boost performance for different uses. |
|
Physical Characteristics |
Bending or flattening changes how well it works, but you can shape it to fit your device. |
|
Advanced Techniques |
New fibers inside the pipe help move heat even faster. |
This flexibility means you can use Heatpipe Cooling in laptops, gaming consoles, or machines.
Do you hate noisy fans? Heatpipe Cooling works quietly. It doesn’t need moving parts or extra power. The heat moves on its own. That means you won’t hear buzzing or whirring.
No moving parts means no noise.
The system runs by itself. You don’t have to turn it on or off.
It uses very little energy. This makes it efficient and eco-friendly.
|
Evidence Description |
Key Points |
|---|---|
|
Gravity Loop Heat Pipe Principle |
Works with gravity and phase change, so it’s silent and reliable. |
|
Passive Cooling Characteristics |
No active parts, so it’s always quiet. |
|
Low Operating Noise |
Runs with almost no sound and very little electricity. |
You can enjoy a peaceful environment while gaming, working, or relaxing.
Space matters, especially in small gadgets. Heatpipe Cooling systems are smaller and lighter than other cooling setups. You can fit them into thin laptops, tablets, or tiny electronics.
|
Cooling System Type |
Heat Transfer Efficiency |
Size |
Weight |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Air Cooling |
Lower |
Larger |
Heavier |
|
Liquid Cooling |
Higher |
Smaller |
Lighter |
|
Heatpipe Cooling |
High |
Small |
Light |
You get more room for other parts and a lighter device.
You want to save money, right? Heatpipe Cooling can help with that. The starting price might be higher than air cooling. But you save money over time. These systems last long and need little maintenance. In big setups, liquid cooling can be 2.5 times cheaper to run than air cooling. Heatpipe Cooling also keeps costs down as your devices get stronger.
Lower operating costs over time.
Fewer repairs and replacements.
Good value for home users and businesses.
You don’t want your cooling system to fail. Heatpipe Cooling is built to last. Some heat pipes have worked for seven years at 200 °C without problems. Many can last 10 to 20 years, and some even longer. If you pick the right materials and design, your system can last longer than your device.
|
Factor |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Wick Material Compatibility |
Helps the system run smoothly for years. |
|
Mechanical Behavior |
Stays strong, even under stress. |
|
Average Lifespan |
10.5 to 29 years, depending on the type. |
|
Failure Time |
Can range from 12 to 60 years. |
Tip: A reliable cooling system means less downtime and fewer headaches for you.
Heatpipe Cooling costs more at first than air cooling. Air cooling is usually the cheapest option. Liquid cooling can cost even more than Heatpipe Cooling. Here’s a table that shows the starting prices:
|
Cooling System |
Upfront Cost |
|---|---|
|
Air Cooling |
Lower |
|
Heatpipe Cooling |
Moderate |
|
Liquid Cooling |
Higher |
If you want to spend less right away, air cooling is better. Heatpipe Cooling saves money later, but you pay more at the start.
Heatpipe Cooling works best when it is upright. Gravity helps the liquid move back to the hot end. If you tilt or flip the system, it cools less. Here’s a table that shows how much power it can handle:
|
Orientation |
Maximum Power (Qmax) |
|---|---|
|
Gravity-aided |
127 watts |
|
Horizontal |
68 watts |
|
Against gravity |
8 watts |
If your device moves or tilts, you could have problems. The system does not cool well if it fights gravity.
Tip: Check how your device sits or moves before you choose this cooling method.
Heatpipe Cooling works best at higher temperatures. If your device stays cool, it may not work as well. Other cooling systems work better at low temperatures. Here’s a table to compare them:
|
Cooling Technology |
Effective Temperature Range |
Performance Improvement |
|---|---|---|
|
Heat Pipe (HP) |
Higher temperatures |
Improved COP by 42% |
|
Thermoelectric (TE) |
Lower temperatures |
Improved cooling capacity by 53% |
|
Vapor Compression Refrigeration (VCR) |
Lower temperatures |
Capable of dissipating 200 W/cm² at lower temperatures |
If you need to cool something that is always cold, try another system.
When you turn on your device, Heatpipe Cooling needs to warm up. The liquid inside must heat up to work well. You might notice a short wait before your device feels cool. Most people do not mind this, but it is good to know.
Heatpipe Cooling uses a sealed tube with liquid inside. If the tube breaks, the liquid can leak out. This does not happen often, but it is possible. If there is a leak, the cooling system will stop working. You may need to replace the heat pipe. Most devices protect the pipes, but accidents can still happen.
Note: Be careful with your device so you do not damage the cooling system.
Heatpipe Cooling is not good for very hot devices. Most heat pipes can only handle less than 25 watts. If you need to cool something hotter, you need a special design. These custom systems can handle over 150 watts, but they cost more. They also need careful planning. High heat can cause problems like dry-out or bad performance if the pipe is not set up right.
Standard heat pipes handle less than 25 W.
Custom designs can go above 150 W but need low thermal resistance.
High heat loads can cause problems, like dry-out or poor cooling if not set up right.
If your device gets very hot, you should look at other cooling choices.

You probably know air cooling. Most computers and gadgets use fans to blow air over hot parts. This method is simple and cheap. You can fix or replace fans easily. But fans can get noisy and need cleaning. Dust builds up and slows them down. Over time, fans wear out and need more attention.
Here’s a quick look at how air cooling compares to Heatpipe Cooling:
|
Cooling System Type |
Maintenance Requirements |
Key Features |
|---|---|---|
|
Heat Pipe Cooling |
Minimal maintenance due to passive design and no moving parts |
Uses phase-changing coolant, closed-loop system, no energy needed for heat transfer |
|
Air Cooling |
More frequent maintenance due to mechanical components |
Needs fans for air movement, parts wear out over time |
You save time with Heatpipe Cooling because you don’t have to worry about fan problems.
Liquid cooling uses pumps and tubes to move coolant over hot spots. This system works well for very powerful computers or big machines. You get great cooling for high heat loads. But liquid cooling is more complex. You need to watch for leaks and keep the system clean. Sometimes, pumps break or coolant runs low.
Let’s compare how Heatpipe Cooling and liquid cooling handle heat:
|
Cooling Method |
Performance Characteristics |
|---|---|
|
Good for small spaces and hot spots. Works best for local heat management. |
|
|
Liquid Cooling |
Handles high power. Best for big jobs, but needs more care and can be less reliable. |
|
Cooling Method |
Mechanism of Heat Transfer |
|---|---|
|
Heatpipe |
Uses vaporization, which moves heat faster than liquid cooling. |
|
Liquid Cooling |
Stores heat in the liquid, which is less efficient than vaporization. |
|
Cooling Method |
Thermal Design Power Capability |
|---|---|
|
Liquid Cooling |
Can cool processors up to 350 W and accelerators up to 700 W. |
Liquid cooling wins for super-hot devices, but you deal with more parts and possible problems.
You might ask, “When should I pick Heatpipe Cooling?” Here are some tips:
You want a quiet system with no moving parts.
Your device has a tight space or odd shape.
You need low maintenance and long life.
You care about saving energy and lowering costs.
Your device does not get extremely hot.
Heatpipe Cooling also helps save energy. Some systems cut energy use by up to 80% and lower CO2 emissions by 63% to 80%. If you want a simple, silent, and efficient way to keep things cool, this method is a smart choice.
Tip: If you use a laptop, tablet, or small electronics, Heatpipe Cooling fits your needs best.
Heatpipe cooling works well because it moves heat fast. You can use it in many shapes, and it runs quietly. But there are some problems. It costs more, needs gravity to work best, and only works in certain temperatures. Before you choose this system, think about these things:
What temperature does your device reach?
How much heat do you need to move?
Does your device have enough space or a special shape?
How much money can you spend?
Lots of people in technology and factories use heatpipe cooling. They trust it because it works for a long time and does not break often. Think about the good and bad points. The best cooling system is the one that fits what you need most.
You should check your device’s size, heat level, and how it sits. If you want quiet cooling and your device doesn’t get super hot, heatpipe cooling works well. Laptops, tablets, and small gadgets often use it.
You can add heatpipe cooling to some devices, like desktop computers. You need to follow the instructions and handle parts gently. If you feel unsure, ask a professional for help.
If a heat pipe leaks, the cooling stops working. You might notice your device gets hot fast. You should replace the broken part. Most devices protect heat pipes, so leaks rarely happen.
You don’t need to clean or oil heat pipes. They work on their own. You can check for damage once in a while. If you see cracks or leaks, replace the pipe. Otherwise, just enjoy the quiet cooling!
By continuing to use the site you agree to our privacy policy Terms and Conditions.